|
Proxy Server
2.0
Installation
Minimum
requirements for Proxy Server 2.0
-
486 or higher
CPU
-
24MB RAM (with Intel
processor)
-
32MB RAM (with RISC
processor)
-
10MB free hard drive
space
-
5MB required minimum
free hard drive space for caching. (Although it is
recommended you have 100MB + 0.5MB per client)
-
NT Server 4.0 with
Service Pack 3 installed.
SETUP.EXE can
be used to install Proxy Server.
Options
-
/r - Reinstall Proxy
Server
-
/u - Uninstall Proxy
Server
-
/k "keynumber" -
Specifies the CD Key
Proxy Server
2.0 is added into the MS Management Console (Internet
Service Manager) administration
utility.
Client Installation
Client
software can be installed through the
//servername/mspclnt share and running SETUP.EXE, or
by connecting to http://servername/msproxy and
running the installation program.
MPCSETUP.LOG
- Log file displaying problems found during client
installation.
The following
items are installed with the client software
-
WinSock Proxy client
application
-
MSPCLNT.INI - Contains
client configuration information.
-
MSPLAT.TXT - Contains
the Local Address Table.
Cache
Recommended
cache space allocation is 100MB + .5MB free disk space per
client.
The default
setting for cache is 100MB when the drive has at least 150MB
free hard drive space.
Caching can
only be performed on an NTFS partition. It cannot be
performed on a FAT partition.
To convert a
FAT partition to NTFS to allow caching, use the CONVERT.EXE
utility.
Connections
requiring authentication or SSL connections will not be
cached.
Passive
caching
All objects are cached. Cached objects will be
removed after their TTL has expired. Objects will then be
re-cached only when a client accesses that site
again.
Active
caching
Frequently requested objects are retrieved from
the Internet by the proxy server when the TTL of the object
in cache is getting ready to expire.
Caching
options
Cache expiration
policy
-
Updates are more
important - Lowers cache performance to keep popular pages
updated frequently.
-
Equal importance -
Balances cache performance with cache updates.
-
Fewer network accesses
are more important (more cache hits) - Provides best cache
performance.
Enable
active caching
-
Faster
user response is more important - Saves less cache, but
updates what is saved very frequently. Causes more users
to access data from the Internet rather than
cache.
-
Equal
importance - Balances cache performance with cache
updates.
-
Fewer
network accesses are more important - Allows least amount
of Internet traffic and will not update cache as
often.
To limit the
size of cache objects, use expired objects in the cache, or
change an object's TTL, set the proper options in the page
accessed through the Web Proxy Service Properties window by
clicking the Caching tab, then click Advanced.
Cache
Filters
List of specific URLs that are in the cache. You
can edit the cache list in the Web Proxy Service Properties
window by clicking the Caching tab, Advanced, then click
Cache filters.
LAT
(Local Address Table)
LAT -
Contains IP addresses of the internal network and IP address
of the proxy server.
MSPLAT.TXT -
Contains the Local Address Table. The master copy of this
file is stored on the server, and can be downloaded to
client systems.
LOCALLAT.TXT
- Custom LAT for clients that need access to network ranges
not specified in the MSPLAT.TXT You can
construct the list of internal IP addresses by clicking
Construct Table.
Add Internal
IP ranges from your network to specify addresses of clients
that will be connecting throught the proxy
server.
IP ranges can
be changed in the individual service's properties by
clicking the Local Address Table
button.
CARP
(Cache Array Routing Protocol) and Multiple Proxy
Servers
CARP -
Multiple proxy servers are configured in an array to provide
a single logical cache. These servers communicate with each
other, so that each server knows the exact contents of the
other servers. This disallows cache
duplication.
Uses HTTP to
communicate.
CARP can be
implemented on clients using PAC - Proxy Auto-Config
file.
Proxy arrays
use an array membership list. They use TTL to determine when
to check for active servers, and maintains the list of
active servers in the array membership list.
Array manager
is used to maintain the array membership list. List includes
TTL until next check, URL to receive array information for a
remote manager, and load factors for each server.
The proxy
server will query array for a new table when TTL
expires.
Heirarchical
routing Requests are forwarded from a downstream proxy or
array to an array of upstream proxies when they cannot be
serviced. One hop is performed in each array before being
forwarded to the next level.
Distributed
routing
One member of the array will answer a request
received by another member of the array, when it is
determined that they are the highest scoring proxy (through
hash-based routing).
Hash routing
Computes list of available servers and the URL to
determine which proxy server in the array to
use.
Array members
contain a script, written in JavaScript, which tells clients
how to connect to the array.
To view the
array membership table, input the following URL into your
browser
The list you
will receive will resemble the following:
server1
192.168.0.1 80 http://server1:80/array.dll MSProxy/2.0
7521 Up 100 150
server2 192.168.0.2 80
http://server2:80/array.dll MSProxy/2.0 7521 Up 100
150
The table
describes the information for server1
|
servername
|
server1
|
|
IP Address
|
192.168.0.1
|
|
Port number
|
80
|
|
URL for array.dll
|
http://server1:80/array.dll
|
|
Version of Proxy Server
|
MSProxy/2.0
|
|
Number of seconds in current state
|
7521
|
|
Current state (up or down)
|
Up
|
|
Load factor of server
|
100
|
|
Cache size
|
150
|
Under the
Routing tab of the proxy's properties, you can configure
Upstream routing to automatically forward client requests to
the Internet or to another proxy server or array.
Under the
Routing tab of the proxy's properties, check the Enable
backup route box and insert the proper parameters to
automatically forward requests to the Internet or another
proxy server or array in case the first upstream choice is
unavailable.
Routing within
the array can be enabled to resolve proxy requests within
the array prior to routing the client to an upstream server
or array. This allows load balancing within the
array.
Administration
Proxy Server
can be administered through the Internet Service Manager and
through the command line.
Proxy Server
installs counters into Performance monitor to enhance and
troubleshoot more efficiently.
To remotely
administer Proxy server, you must have the same version of
client software installed on your system as the server you
are connecting to.
Command line
utilities
-
REMOTMSP - Used to
remotely configure and administer Proxy Server, including
starting and stopping services, backing up and restoring
proxy information, and managing server arrays.
-
WSPPROTO - Used to
remotely edit service protocol definitions.
To stop/start
services from the command line
-
Web - NET STOP|START
W3SVC
-
WinSock - NET
STOP|START WSPSRV
-
Socks - NET STOP|START
W3SVC or use Remotmsp.exe
Backup
and Restoration
Proxy server
parameters are backed up to a text file in the C:\MSP\CONFIG
directory, unless otherwise specified.
To perform a
backup, go to the Properties field of any proxy service,
click the Service tab, then click Server
Backup. Select the directory you would like to backup to
and click OK.
To perform a
restoration, go to the Properties field of any proxy
service, click the Service tab, then click Server
Backup. Select whether to perform a Partial or Full
Restore, then specify the directory that the backup was
placed in and click OK.
Partial Restore -
Method is a non-computer specific restore; Items such as
array membership and logging information will not be
restored.
Full Restore - Method
is a computer specific restore; All items are restored.
Security
To prevent
unauthorized access to your network from external users
Disable IP forwarding
in TCP/IP section of the Control Panel/Network
configuration screen.
Do not add external
addresses to the LAT.
Deny listening on
inbound service ports.
Authentications
Anonymous - Any user
is able to access the site.
Basic - Login and
Password are necessary to access the site.
Windows NT
challenge/response - Uses current login information to
allow/disallow access to site. Only available in same or
trusted domains.
Challenge/response will only work properly with IE
3.0 and later. When a non-IE browser accesses a
challenge/response site, access will be denied.
Web and
Winsock proxy
Within the
Web proxy and WinSock proxy properties screens, you can
choose which users/groups are able to access the Internet
through particular protocols. Permissions must be assigned
separately to each protocol.
Web proxy
covers only FTP, Gopher, Secure and Web protocols. The web
protocol covers HTTP and HTTPS protocols. The secure
protocol covers protocols setup to use secure
ports.
WinSock proxy
covers many protocols including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, Telnet,
Gopher, IRC, RealAudio, POP3, SMTP, and others.
Once users
have been assigned permissions to a protocol, they then have
access to the Internet through those specified ports. For
example, when a user is assigned permission to use HTTP,
they then have access to the Internet through port
80.
To assign or
revoke permissions for users to other protocols, highlight
the user and click Copy to or Remove From,
select the proper protocol, and click OK.
WinSock proxy
allows Unlimited Access to be specified. This allows
all users full access to all ports on that defined in the
WinSock proxy service.
WinSock proxy
protocols can be edited, or new protocols can be added, to
customize or create ports that are needed for certain
application communications. Protocols can also be defined to
only allow outbound or inbound access.
Socks
proxy
Socks proxy
uses the Identification protocol and IP addresses to
authenticate clients.
Socks proxy
service depends on the Web proxy service to be running. If
the Web proxy service stops, the Socks proxy service also
stops.
Socks proxy
does not support IPX/SPX.
Socks
permissions can be moved change the orders of the listed
permissions.
Custom Socks
permissions can have functions matched to specified port
numbers:
Socks can be
set to deny or allow access from specific IP ranges, domain
names, or all users. Options for this can be set to
Socks port
settings are defined by the following determiners
|
EQ
|
Equal to
|
|
NEQ
|
Not equal to
|
|
GT
|
Greater than
|
|
LT
|
Less than
|
|
GE
|
Greater than or equal to
|
|
LE
|
Less than or equal
to
|
For example, you can choose to
deny access to any port greater than 80 by specifying
Deny in the Action box, GT in the Port box,
and 80 in the Port number field.
Another
example is portrayed in the following graphic
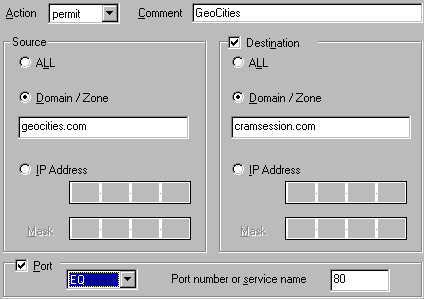
This allows
all clients from geocities.com to access anything in
cramsession.com through port 80.
Identification (Identd) protocol - Provides a false
user name to servers that block MS Proxy clients, to allow
them to access the server's services. Is installed by
running IDENTD.EXE --INSTALL. Is run through the NET
command: NET START|STOP IDENTD.
Domain
Filtering
Domain
filtering is used to grant or deny client access to certain
domains/IP addresses.
Click the
checkbox next to Enable Filtering to allow
filtering.
Options
You can grant
or deny access to
-
Single computer - Must
specify the IP address of a specific system. Can click the
ellipsis button next to the IP field, and specify a DNS
name. It will then return the IP address of that DNS
name.
-
Group of computers -
Must specify the IP address and subnet mask of the
systems.
-
Domain - Must specify
the domain name to grant or deny access to.
Packet
Filtering
Must have an
external network interface before this can be enabled. If
using a modem or ISDN adapter as the external network
interface, you must have RAS Auto Dial setup. Only the
external network adapter will provide packet filtering.
Provides
filtering on packets, addresses and
spoofs/attacks.
All packet
types will be blocked, except for those specified in the
Exceptions list.
Alerts
Proxy server can send alerts for
events through the Event Viewer, log files or
email.
Alerting can
only be enabled when packet filtering is enabled.
Alerts can be
sent for
Rejected packets -
Notifies you when numerous packets are being rejected in
high rates. Rates can be set to alert you when rejected
packets occur at a certain frequency. High frequency rates
can mean an attack is taking place.
Protocol violations -
Notifies you when packets or frames are dissimilar from
the typical protocol structure.
Full disk drive
warnings - Notifies you when disk drive that holds the
service or packet logs is full.
Reverse
Proxy Servers
A reverse
proxy server services requests made to an internal web
server. It will serve as a "firewall" by only letting
visitors through one port to retrieve the information.
Reverse
hosting can be enabled to allow multiple web servers to be
contacted through the reverse proxy server.
To enable
reverse proxy support, under the Publishing tab of the proxy
service properties panel, click the Enable Web publishing
box. There are three options available
Discarded - All web
server requests will be discarded.
Sent to the local web
server - All requests will be sent to the default web
server.
Sent to another web
server - All requests are sent to a specific web
server.
To create a
reverse host route, click Add. In the Path field, insert the
URL to be routed. In the URL field, insert the URL of the
internal web server that will service this
request.
Logging
Log files
are stored in the C:\WINNT\SYSTEM32\MSPLOGS\ directory by
default.
-
W3filename.LOG
- Web Proxy service log
-
WSfilename.LOG
- WinSock Proxy service log
-
SPfilename.LOG
- Socks Proxy service log
-
PFfilename.LOG
- packet filters
filename =
yymmx; yy=year, mm=month,
xx=day/week/month of log.
Logging to a
text file takes considerably less resources than logging to
database.
An OBDC driver
must be installed on the proxy server to be able to log to a
database.
A DSN (Data
Source Name) must be added to describe which server or
database file you are writing to.
MPKLOG.EXE -
Included with Proxy Server. Tool to create SQL tables for
proxy server logging.
-
Common Port
Numbers
-
|
FTP
|
21
|
|
Telnet
|
23
|
|
SMTP
|
25
|
|
Gopher
|
70
|
|
HTTP
|
80
|
|
POP3
|
110
|
|
PPTP
|
1723
|
-
Proxy
Clients
Proxy Server
does not support IPX on Windows 3.x clients.
Windows 3.x
clients cannot use the WinProxy service, but can use the
Socks and Web services.
Windows 95
clients must have the Novell Client 32-bit IPX stack
installed in order use IPX through the proxy
server.
The default
URL for clients to get the array routing script is
http://servername/Array.dll?Get.Routing.Script
To prevent
Exchange clients from connecting to Internet POP3 servers,
put DISABLE=1 under the [EXCLNT32] header in the MSPCLNT.INI.
Clients with
the WinSock proxy client application download the
MSPCLNT.INI file every time the client system is restarted,
and every six hours after the last refresh.
WSPCFG.INI -
Contains server proxying information pertaining to the local
client. It will never be overwritten by the server. This
file contains application-specific settings for each WinSock
application.
-
RAS (Remote
Access Services)
RAS is
capable of using the following connection protocols
RAS supports
call back security to either the calling number or to a
specified, non-changing number.
RAS for NT 4.0
supports multilink (the use of more than one modem to
achieve higher transmission speeds). Multilink cannot
be used with callback security unless there are two
(or more) ISDN modems configured on the same phone
number.
RAS uses
NetBEUI as the default network protocol, but can also use
TCP/IP and IPX/SPX. TCP/IP will need to be used if you are
using programs that utilize the Windows Sockets (Winsock)
interface over the RAS services.
RAS encryption
settings
|
Allow any authentication including clear text
|
This will allow RAS to use a number of password
authentication protocols including the Password
Authentication Protocol (PAP) which uses a plain-text
password authentication. This option is useful if you
have a number of different types of RAS clients, or to
support third-party RAS clients.
|
|
Require encrypted authentication
|
This option will support any authentication used
by RAS except PAP.
|
|
Require Microsoft encrypted authentication
|
This option will only make use of Microsoft's CHAP
(Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol). All
Microsoft operating systems use MS-CHAP by
default.
|
|
Require data encryption
|
This option will enable the encryption of all data
sent to and from the RAS
server.
|
RAS will write
to a log file which can be used for troubleshooting RAS
services. In order to enable RAS to write to the log, you
have to enable it in the Registry.
Auto Dial is
used to automatically dial-up to the Internet when a client
is attempting to gain Internet access through the Proxy
Server with RAS Auto-dial capabilities.
A RAS
phonebook entry to your ISP will need to be created to allow
Auto Dial to work. Credentials can be setup to set the user
name and password used to connect with the ISP.
When Auto Dial
is configured for the first time, or if settings are
cleared, the services will need to be restarted before
settings can take effect.
Computer
name resolution
-
DNS (Domain
Name Services) - Used to resolve DNS host name to an IP
address.
-
WINS
(Windows Internet Naming Service) - Used to resolve NetBIOS
computer name to an IP address.
-
HOSTS - File
which contains mappings between DNS host names and their IP
addresses.
-
LMHOSTS -
File which contains mappings between NetBIOS computer names
and their IP addresses.
-
|

