|
Physics - 1998 ( I.S.C)
You are on
Questions-1 to 5
(Three
hours)
Answer all questions in Part I and six
question from part II, choosing two questions from each of the
sections A,B and C .
All working,
including rough work, should be done on the same sheet as, and
adjacent to, the rest of the answer.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are
given in brackets [ ] .
(Material to be supplied ; Log tables including
Trigonometric functions).
PART I
(Compulsory)
Q1, Answer
all questions briefly and to the point:
(i) Define 'electric potential' at a point in an electric
field.
(ii) A capacitor is charged through a
potential difference of 200v when 0.1C charge is stored in it. How
much energy will it release when it is discharged?
(iii) Find out the resistivity of a
conductor in which a current density 2.5 A/m2 is found to
exist when an electric field 15 V/m is applied on it.
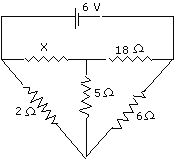
(iv) Find out the magnitude of resistance
X in the given circuit diagram (fig.1) when no current flows through
the 5W resistor.
(v) Define magnetic 'permeability'.
(vi) Write an expression for the magnetic
field produced by an infinitely long straight wire carrying a
current i, at a short perpendicular distance 'a' from itself.
(vii) A bar magnet placed in a uniform
magnetic field of strength 0.3 T, with its axis at 30° to the field,
experiences a torque of 0.06 Nm. What is the magneitc moment of the
bar magnet?
(viii) With reference to alternating
currents and voltages, state any one fundamental difference between
'resistance' and 'reactance'.
(ix) Define the term 'coherence' for
light waves.
(x) A plane diffraction grating is used
with a monochromatic source of wavelenght 5000 Å under normal
incidence. The second order maximum is obtained at a diffraction
angle of 30°. Find the grating element.
(xi) A monochromatic ray of light is made
to fall on a normal 60° prism under minimum deviation condition.
What is the relation between the angle of incidence and the angle of
emergence?
(xii) Find the radius of curvature of the
convex surface of planocovex lens whose focal length is 0.3 m and
the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5.
(xiii) What happens to the
wavelength of a photon after it collides with an electron?
(xiv) What should be done to increase the
intensity of X-rays, produced by a Coolidge Tube?
(xv) The radius of the first electron
orbit of hydrogen atom is 5.3 x 10-11 m. What is the
radius of the second orbit?
(xvi) What is meant by the term
'isotope'.
(xvii) Give the relation between 'half
life' and 'disintegration constant' of a radio-active
material.
(xviii) When 3Li7
is bombarded with a certain particle, two alpha particles are
produced. Identify the bombarding particle.
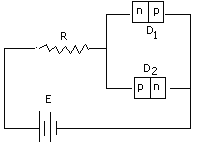
(xix) Fig.2 shows two p-n junction diodes
along with a resistance R and a dc battery E. Indicate the path and
direction of flow of appreciabe current in the circuit.
(xx)What kinds of baising are required to
the collector and base of a transistor in a common emmiter
amplifier?
PART II
Answer
six questions from Part II, choosing two questions from each of the
sections A,B and C.
SECTION A
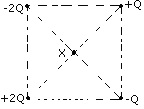
Q2. (a) Fig.3
Shows four point charges at the corners of a square of side 2 cm.
Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field at the centre
(X) of the square if Q = 0.02m C.
[Use 1/4pÎ0 =
9x109 Nm2 C-2].
(b) What is meant by 'capacitance'?Give
its S.I unit.
(c) In Fig.4C is a large value capacitor
connected ion series with a centre zero galvanometer G, a dec
battery E and key K.
What will be observed in G when K is
suddenly closed? Give reasons for your answer
Q 3 (a)When the key K is closed
then the capacitor starts getting charged. The upper plate is
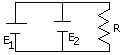
positively charged and the lower plate is negatively charged. 3.(a) The circuit diagram in fig.5
has two cells E1 and E2 with emf 4V and 2V respectively, each one
having an internal resistance 2W.
The external resistance R is of 8W. Find the magnitude and
direction of the currents flowing through the two cells.
(b) Fig.6 shows a cell with emf E and
internal resistance r, connected to a voltmeter V and a variable
resistance R. Deduce the relatiuonship between V, E, R and r. How
will the value of V vary when R is reduced?
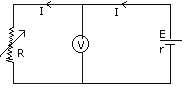
Q 4 (a)I = E/R +r
IR = E
- Ir ---------------(1)
V =IR where V is potential drop
across R
When R is reduced, I increases .So V is
decreased. length of the dipole is 2l
and its magnetic moment is M.
(b) Why is it possible to make permanent
magnets out of steel?
(c) The radius
of the first electron orbit of hydrogen atom is 0.5 A. The electron
moves in this orbit with a uniform speed of 2.2x106 m/s.
What is the magnetic field produced at the cnetre of the nucleus due
to the motion of this electron? (Use m0/4p = 1x10-7 N/A2 and electronic
charge = 1.6x10-19C).
Q 5.(a) Define
'coefficient of mutual inductance' for a pair of coils.
A
solenoidal coil has 50 turns per cm along its length and a
cross-sectional area of 4 cm2. 200 turns of another wire
is wound round the first solenoid coaxially. The two coils are
elctrically insulated from each other. Calculate the mutual
inductance between the two coils. (Use m0 = 4p x
10-7 N/A2).
(b). A 2mF capacitor,
100W
resistor and 8 H inductor are conected in series with an A.c source.
What should be the frequency of this A.c source for which the
current drawn in the circuit is maximum? If the peak value of emf of
the source is 200V, find for maximum current:
(i) the inductive
and capacitative reactances of the circuit,
(ii)total impedence
of the circuit of the circuit,
(iii)peak value of current in the
circuit,
(iv)the phase relation between voltages acroos inductor
and resistor.
(v)the phase difference between voltages across
inductor and capacitor.
| 